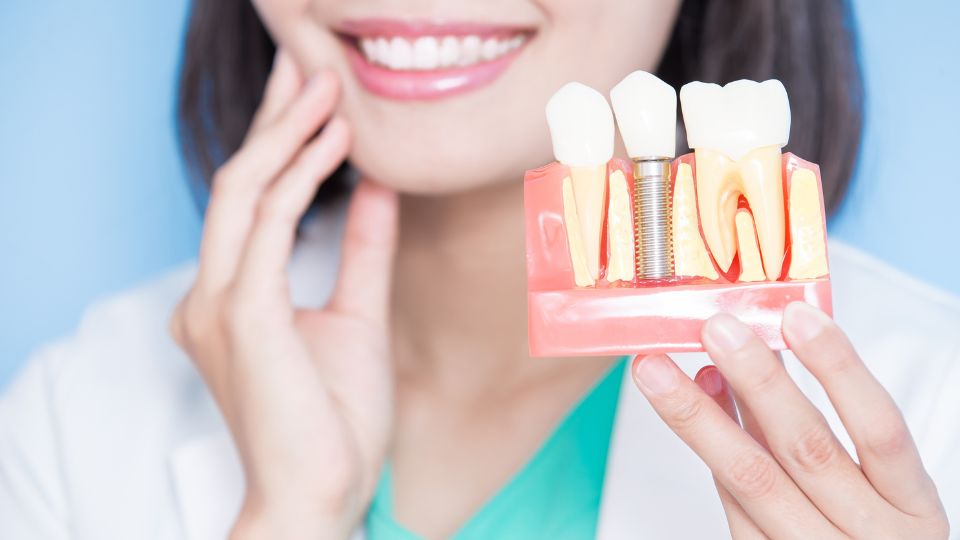
Dental implants are medical devices that are surgically implanted into the jawbone to restore a person's ability to chew or restore appearance. They provide support for artificial (false) teeth such as crowns, bridges, or dentures.
When a tooth is lost due to injury or disease, a person may experience complications such as rapid bone loss, speech problems, or changes in chewing patterns that cause discomfort. Replacing a lost tooth with a dental implant can significantly improve the patient's quality of life and health.
Dental implant systems consist
Dental implant systems consist of a dental implant body and a dental implant abutment and may also include an abutment fixation screw. The body of the dental implant is surgically placed in the jaw bone in place of the root of the tooth. The dental implant abutment is usually fixed to the implant body by the abutment fixing screw and extends through the gums into the mouth to support the attached artificial teeth.
Before deciding on dental implants, talk to your dentist about the potential benefits and risks, and whether you qualify for the procedure.
Things to consider:
Your general health is an important factor in deciding if you are a good candidate for dental implants, how long it takes to heal, and how long the implant can stay in place.
Ask your dentist what brand and model of dental implant system is used and keep this information for your records.
Smoking can impair the healing process and reduce the long-term success of the implant.
The healing process of the implant body can take several months or longer, during which time you usually have a temporary abutment in place of the tooth.
After the dental implant procedure:
Carefully follow the oral hygiene instructions given to you by your dentist. Regular cleaning of the implant and the surrounding teeth is very important for the long-term success of the implant.
Schedule regular visits to your dentist.
If your implant becomes loose or hurts, tell your dentist immediately.
benefits and risks
Dental implants can greatly improve the quality of life and health of a person who needs them. However, complications can sometimes occur. Complications can occur soon after the dental implant is placed or much later. Some complications lead to implant failure (generally defined as loosening or loss of the implant). Implant failure may require additional surgery to repair or replace the implant system.
Advantages of dental implant systems:
- Restores the ability to chew
- Restores the aesthetic appearance
- Helps prevent jaw shrinking due to bone loss
- Preserves the health of surrounding bones and gums
- Helps keep adjacent (close) teeth stable.
- Improve the quality of life
- Risks associated with dental implant systems:
- Damage to surrounding natural teeth during implant placement
- Injury to surrounding tissues during surgery, such as breast perforation
- Injuries during surgery (for example, fracture of the surrounding jawbone)
- Inadequate function, such as the feeling that the teeth are not biting together normally
- Feeling that the tooth is loose or turning out of place due to the loosening of an abutment screw
- Breakage of the implant body (loosening of the implant body)
- due to a systemic infection, which is more likely in patients with uncontrolled diabetes
- due to a local infection in the bones and gums that support the implant body
- due to delayed healing, which is more likely in patients who smoke
- Difficulty cleaning the gums around the implant, resulting in poor oral hygiene
- Untreated periodontitis
- Post-operative numbness due to entrapment or nerve damage
Always inform healthcare professionals and imaging technicians of the presence of dental implants before performing MRI or X-ray procedures. Dental implants can distort or distort these images. The FDA is not aware of any reported side effects with MRI or X-ray procedures involving dental implants.
Methods for Assessing the Safety of dental implants
Dental implant systems are generally made from materials that meet the international consensus standards of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or ASTM International. These standards contain details on what makes a material safe. Most dental implant systems are made of titanium or zirconium oxide. Other materials such as gold alloys, cobalt-based alloys, titanium alloys, or ceramic materials are sometimes used. The safety profiles of these materials are well known.
Dental implant systems are evaluated according to international consensus standards. Biocompatibility testing to show that physical contact with the device does not cause complications such as irritation or allergic reactions is part of the evaluation, which helps to ensure that the materials of the dental implant system are safe and have no adverse effects when implanted in humans.
For manufacturers to market dental implant systems in the United States, they must first demonstrate to the FDA that their systems are as safe and effective as dental implant systems already on the market.